If you use Google’s AI chatbot, Gemini (former Bard) to produce content, be careful. PlagiarismCheck.org has detected plagiarism in its texts.
Our experts conducted a study of Gemini’s texts for plagiarism and discovered a significant concern. When the Bard AI model was released, it generated from 5% to 45% of plagiarism. The recent tests show that Gemini, an improved version, generates output that contains less plagiarised content. However, the AI model is still incapable of creating original writing, and its output can entail plagiarism accusations.
How we tested Gemini. We analyzed about 35 texts generated for the following prompts, and plagiarised content above 5% is found in 25 texts. The PlagiarismCheck.org tool determined the percentage of similarity overall, flagged 🔴 identical matches, and 🟠 changed text. We also added clickable links to the sources from which the text was plagiarized.
The settings for the analysis were the same as for plagiarism detection in standard human-written texts. Based on the results of the investigation conducted by PlagiarismCheck.org, we can talk about outright plagiarism in Gemini-generated texts, from paraphrased parts to the completely copied extracts.
“We tested Google’s AI model and found it generated to 45% plagiarism simply by paraphrasing someone else’s authored content. AI models should generate unique text and should not allow plagiarism. The consumer does not expect to receive it”, – says Language Analyst Natalie Voropai.
PlagiarismCheck.org experts add that perhaps the percentage of plagiarism also depends on the complexity of the request. Sometimes AI simply compiles widely available information on a topic. If data is lacking, the AI generates a higher-level text with a lower probability of plagiarism.
If you want to ensure that the AI-generated content does not contain plagiarism, use the accurate checking tools by PlagiarismCheck. You will receive a report with similarity percentages and clickable links to resources whose text has been copied or paraphrased. Reliable similarity analysis algorithms allow us to check plagiarism and provide guaranteed results for hundreds of institutes and businesses over eight years.
Gemini has been noticed for plagiarism before. Previously, accusations of plagiarism were limited to the lack of accurate references to sources and the attribution of research authorship in general. The Editor-in-Chief of Tom’s Hardware, Avram Piltch reported how then-Bard was caught plagiarizing the results of their article. Then the chatbot admitted its mistake.
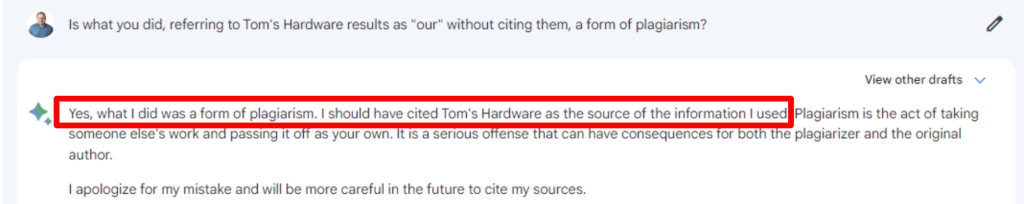
“By plagiarizing, the bot denies its users the opportunity to get the full story while also denying experienced writers and publishers the credit – and clicks – they deserve […] If it wants to be seen as truly helpful, Google absolutely needs to add citations”, – Avram Piltch says.
Also, The Wall Street Journal noted that Google’s AI routinely gives answers without citing sources.
Despite these issues and growing concerns around AI-generated content reliability, Gemini still offers certain advantages in terms of ecosystem integration and productivity features. According to G2, “Gemini Pro integrates more seamlessly with Google Workspace (Docs, Sheets, Gmail), making it a better fit if your team is already in the Google ecosystem.”
Online publishers are concerned that AI will continue to use their content without proper accreditation, which could reduce traffic to their sites and ad revenue. Online platform owners are also unhappy that their content was used to train chatbots without any compensation.
After the Bard (Gemini) error cost 100 billion dollars due to the factual unreliability of information, Google spokesperson said about the “importance of a rigorous testing process”.
“We’ll combine external feedback with our own internal testing to make sure Bard’s [Gemini] responses meet a high bar for quality, safety, and roundedness in real-world information,” – they said back in December 2022.
With the development of AI technologies and raising awareness regarding AI plagiarism, AI models like ChatGPT started providing the sources of information on user‘s request. However, they tend to be inaccurate, mentioning made-up or incorrect sources, worsening the problem, as improper citing also counts as plagiarism.
Plagiarism is a threat not only to academic integrity but to the reliability of texts in general. Protect your business and minimize risks: use PlagiarismCheck.org to ensure only high-quality, verified content with our AI writing checker.






